基于ROS无人小车搭建
writer:lIcht email:lIcht.gzl@gmail.com date: 2019.12.1
一、用仿真的思想解决没有实际里程计的问题以及最重要的基础:tf树的建立。编写假odom欺骗上层导航包,还能达到让小车动的目的,但是误差十分大,但是能在硬件情况不理想的情况下配置上层导航包。
假里程计代码:
x float vx; float vy; float vth;//回调函数,处理速度信息void callback(const geometry_msgs::Twist& vel){ float linear_scale = 1.06; vx = (vel.linear.x/1200) * linear_scale; vy = (vel.linear.y/1200) * linear_scale; vth = (vel.angular.z/1200);}int main(int argc, char** argv){ ros::init(argc, argv, "odometry_publisher"); //节点名称:“odometry_publisher” float x = 0.0; float y = 0.0; float th = 0.0; ros::NodeHandle n; ros::Publisher odom_pub = n.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry>("odom", 50); //订阅cmd_vel速度指令主题,并进入回调函数处理 ros::Subscriber velocity = n.subscribe("cmd_vel", 50, callback); tf::TransformBroadcaster odom_broadcaster; ros::Time current_time, last_time; current_time = ros::Time::now(); last_time = ros::Time::now(); ros::Rate r(10); while(n.ok()){ ros::spinOnce(); // check for incoming messages current_time = ros::Time::now(); //compute odometry in a typical way given the velocities of the robot double dt = (current_time - last_time).toSec(); double delta_x = (vx * cos(th) - vy * sin(th)) * dt; double delta_y = (vx * sin(th) + vy * cos(th)) * dt; double delta_th = vth * dt; x += delta_x; y += delta_y; th += delta_th; //since all odometry is 6DOF we'll need a quaternion created from yaw geometry_msgs::Quaternion odom_quat = tf::createQuaternionMsgFromYaw(th); //first, we'll publish the transform over tf geometry_msgs::TransformStamped odom_trans; odom_trans.header.stamp = current_time; odom_trans.header.frame_id = "odom"; odom_trans.child_frame_id = "base_footprint"; odom_trans.transform.translation.x = x; odom_trans.transform.translation.y = y; odom_trans.transform.translation.z = 0.0; odom_trans.transform.rotation = odom_quat; //send the transform odom_broadcaster.sendTransform(odom_trans); //next, we'll publish the odometry message over ROS nav_msgs::Odometry odom; odom.header.stamp = current_time; odom.header.frame_id = "odom"; //set the position odom.pose.pose.position.x = x; odom.pose.pose.position.y = y; odom.pose.pose.position.z = 0.0; odom.pose.pose.orientation = odom_quat; //set the velocity odom.child_frame_id = "base_footprint"; odom.twist.twist.linear.x = vx; odom.twist.twist.linear.y = vy; odom.twist.twist.angular.z = vth; //publish the message odom_pub.publish(odom); last_time = current_time; r.sleep(); }}
launch里面发布小车的静态tf:
xxxxxxxxxx<launch> <!-- 启动假odom --> <node pkg="fake_odom" type="fake_odometry" name="fake_odometry" output="screen" /> <node pkg="tf" type="static_transform_publisher" name="base_footprint_to_base_link" args="0 0 0.2 0 0 0 /base_footprint /base_link 100"/> <node pkg="tf" type="static_transform_publisher" name="base_link_to_base_laser" args="0 0 0.3 0 0 0 /base_link /base_laser 100"/></launch>
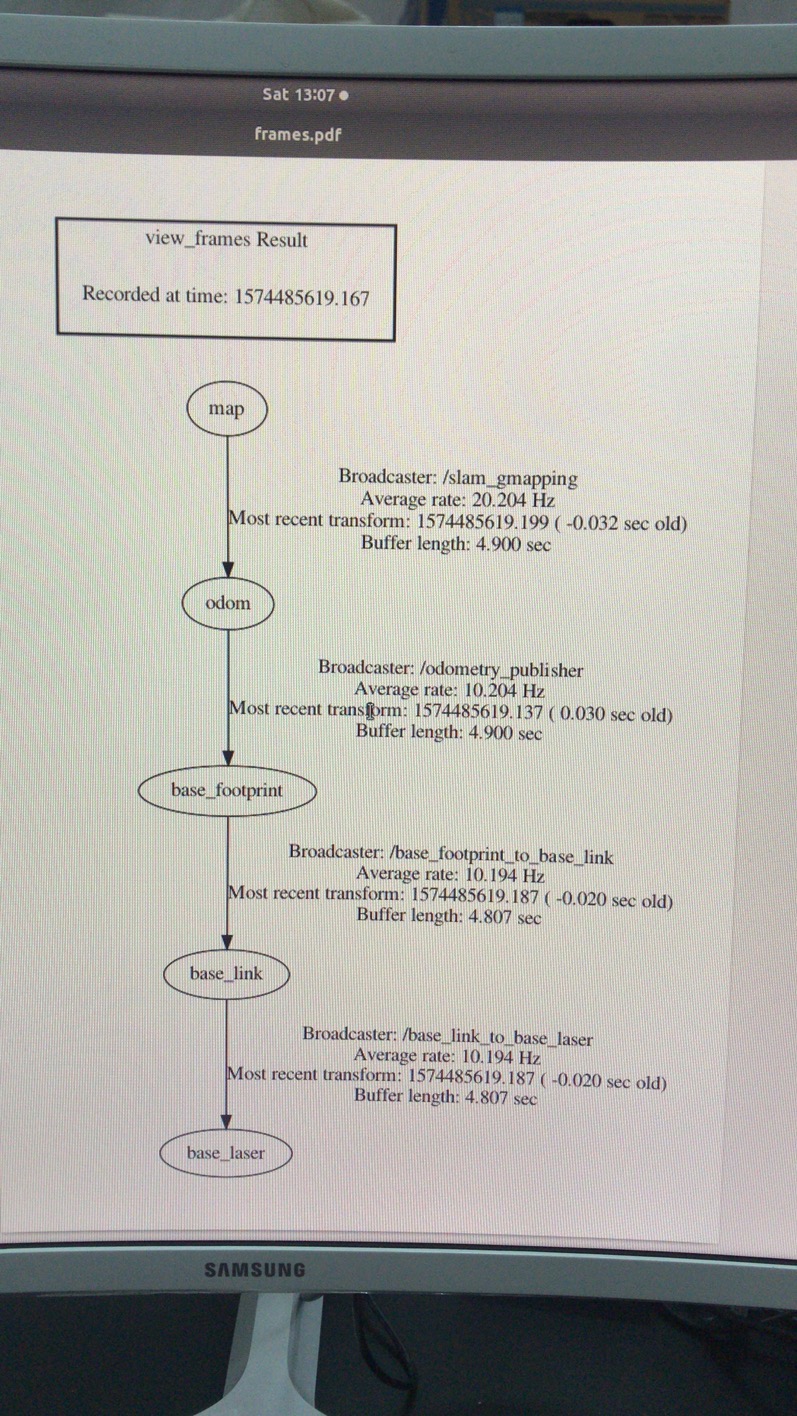
测试验证:odom tf树的成功与否,用teleop发出odom里程计的进口(速度),看tf树时候成功实时变换以及在rviz里面的效果。
tf树成功建立建立与相关节点:
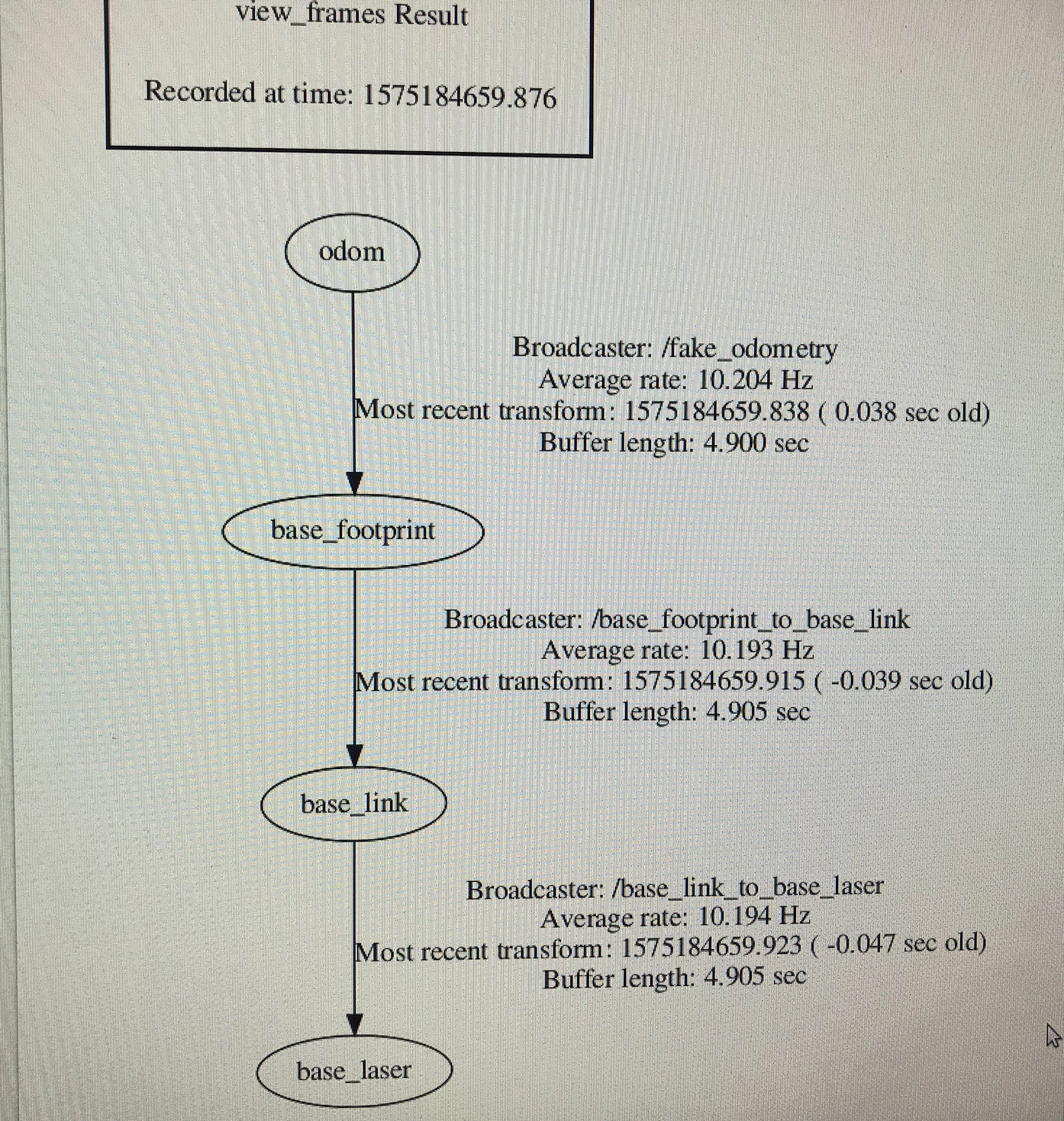
查询odom主题数据:
xxxxxxxxxxcommand: rostopic echo /odom---header:seq: 2510stamp:secs: 1575184851nsecs: 338256423frame_id: "odom"child_frame_id: "base_footprint"pose:pose:position:x: 2.19066214561y: 0.0z: 0.0orientation:x: 0.0y: 0.0z: 0.0w: 1.0covariance: [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]twist:twist:linear:x: 0.176666662097y: 0.0z: 0.0angular:x: 0.0y: 0.0z: 0.0covariance: [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]---
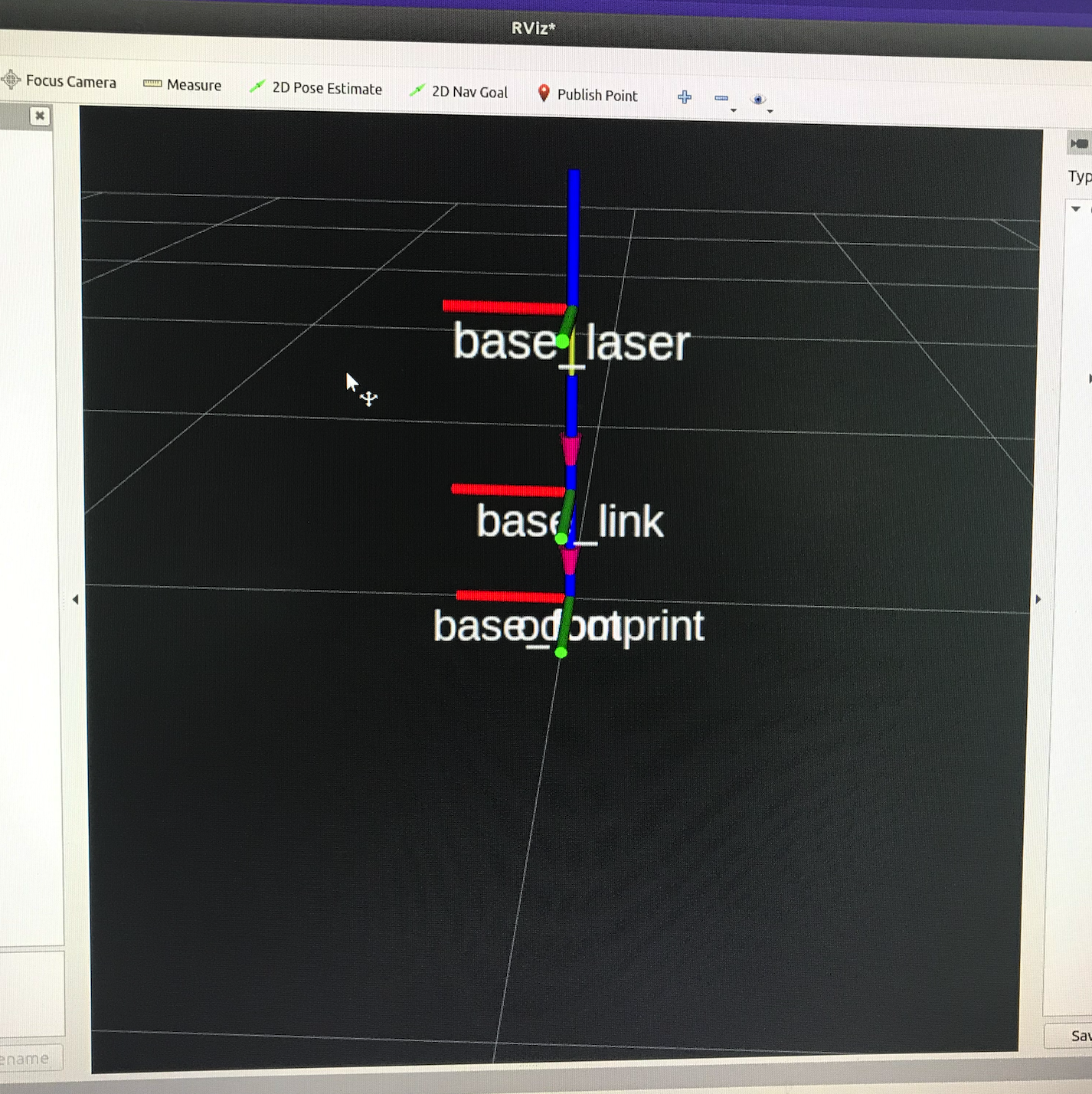
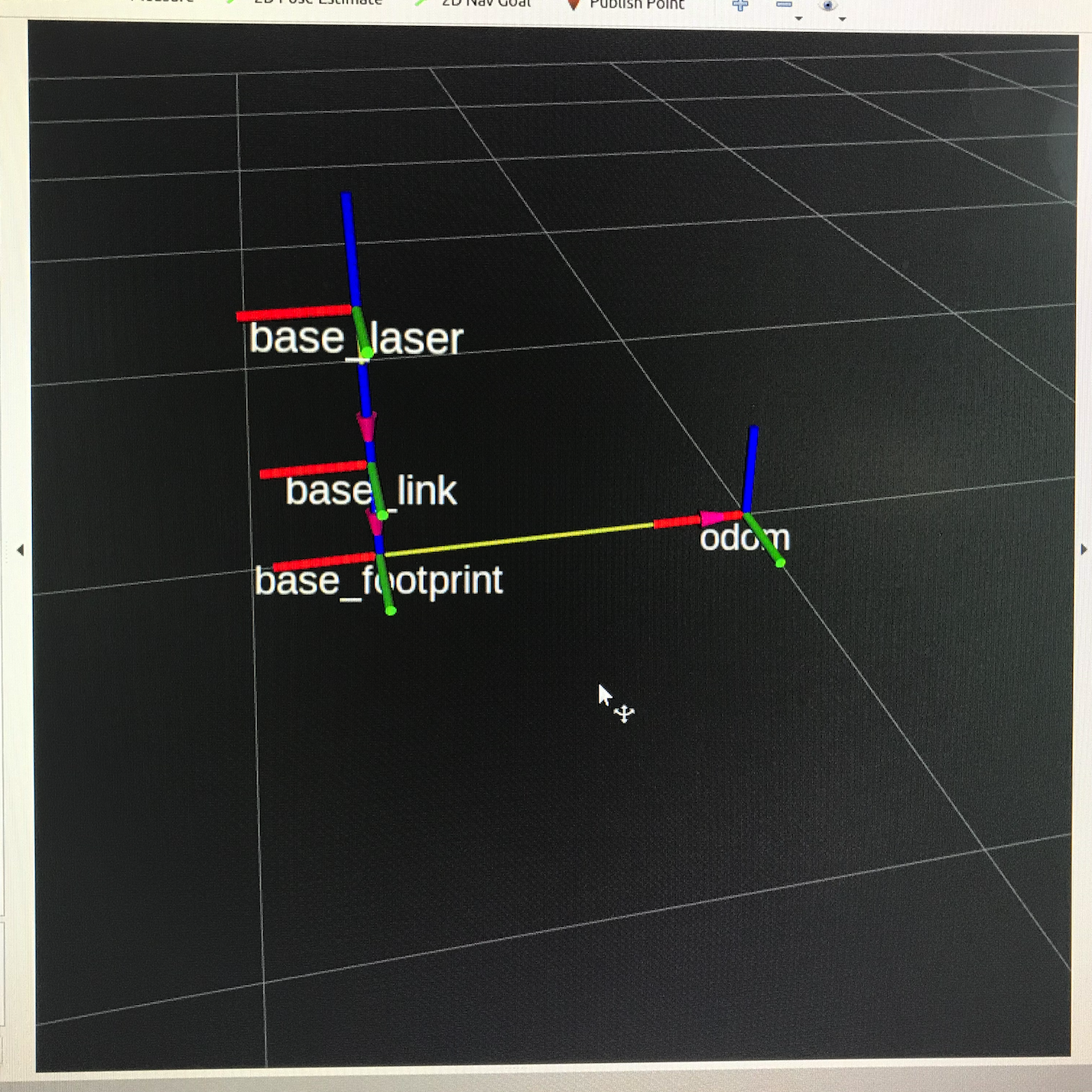
RVIZ里面的运动效果:
二、gmapping 的实现,以及现场跑图的测试。要实现gmapping进行SLAM需要的传感器信息(topic)有:/laser、/odom。需要的tf转换有:laser—>base_link、base_link—>odom。启动rp雷达后便可获得雷达laser信息,这样就满足了gmapping的全部要求。
gmapping参数设置:
xxxxxxxxxx <!-- 启动gmapping --> <arg name="scan_topic" default="scan" /> <node pkg="gmapping" type="slam_gmapping" name="slam_gmapping" output="screen" clear_params="true"> <param name="base_frame" value="/base_footprint" /> <param name="odom_frame" value="odom"/> <param name="map_update_interval" value="2.0"/> <!-- Set maxUrange < actual maximum range of the Laser --> <param name="maxRange" value="10.0"/> <param name="maxUrange" value="5.0"/> <param name="sigma" value="0.05"/> <param name="kernelSize" value="1"/> <param name="lstep" value="0.05"/> <param name="astep" value="0.05"/> <param name="iterations" value="5"/> <param name="lsigma" value="0.075"/> <param name="ogain" value="3.0"/> <param name="lskip" value="0"/> <param name="srr" value="0.01"/> <param name="srt" value="0.02"/> <param name="str" value="0.01"/> <param name="stt" value="0.02"/> <param name="linearUpdate" value="0.25"/> <param name="angularUpdate" value="0.436"/> <param name="temporalUpdate" value="-1.0"/> <param name="resampleThreshold" value="0.5"/> <param name="particles" value="80"/> <param name="xmin" value="-50.0"/> <param name="ymin" value="-50.0"/> <param name="xmax" value="50.0"/> <param name="ymax" value="50.0"/> <param name="delta" value="0.05"/> <param name="llsamplerange" value="0.01"/> <param name="llsamplestep" value="0.01"/> <param name="inverted_laser" value="false"/> <param name="transform_publish_period" value="0.05"/> <remap from="scan" to="$(arg scan_topic)"/> </node>
测试方式:teleop发送伪odom进口数据,建立简单的地图,重点是里程计和雷达数据的成功取用,利用gmapping成功建立地图。
tf树的建立,map坐标成功发布:
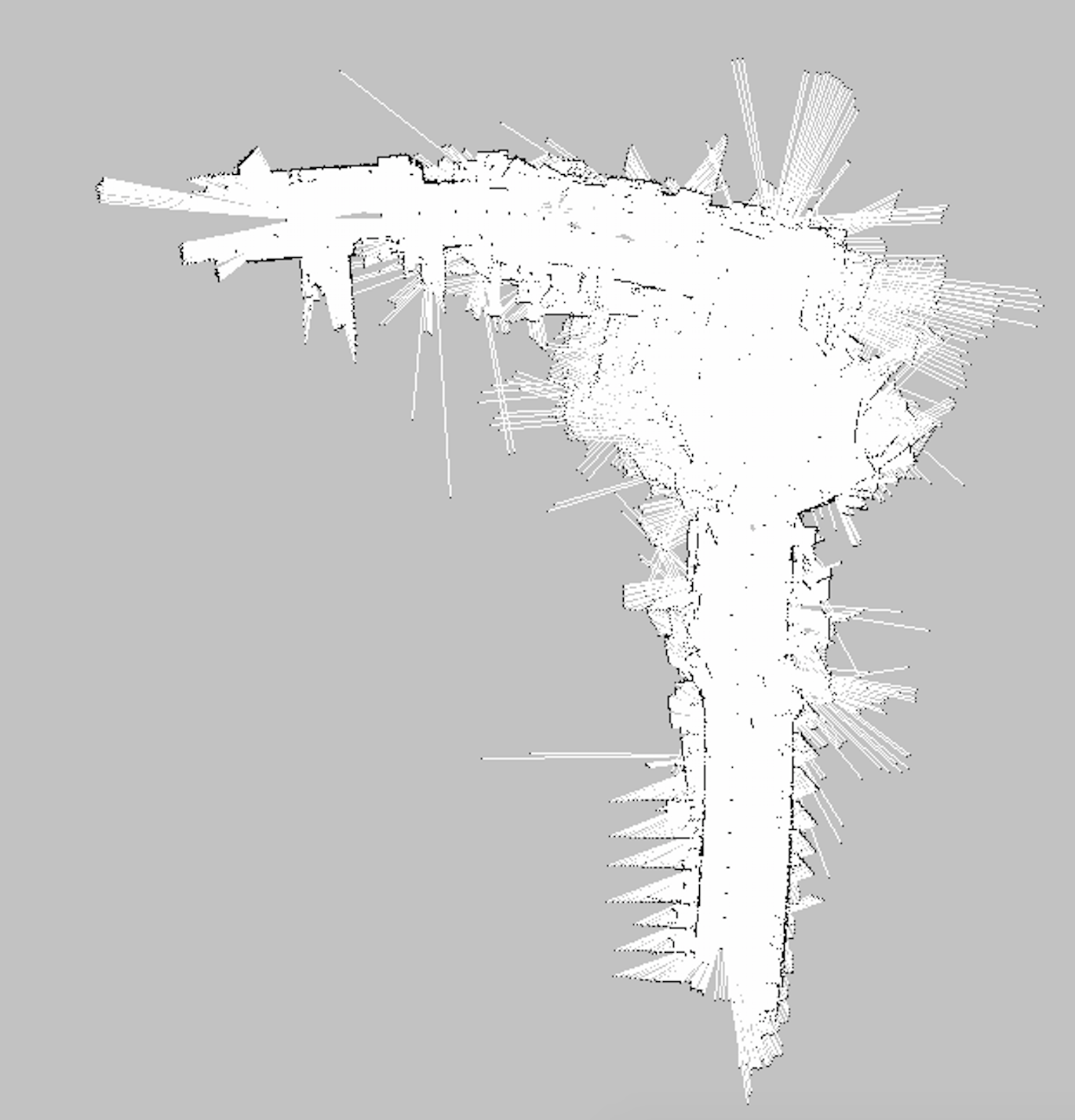
teleop控制小车建立地图:

三、在gmapping可以成功运作后,对move_base及其导航框架的搭建,对move_base里出现的问题:goal off global map,DWA cann't get path等报错的处理
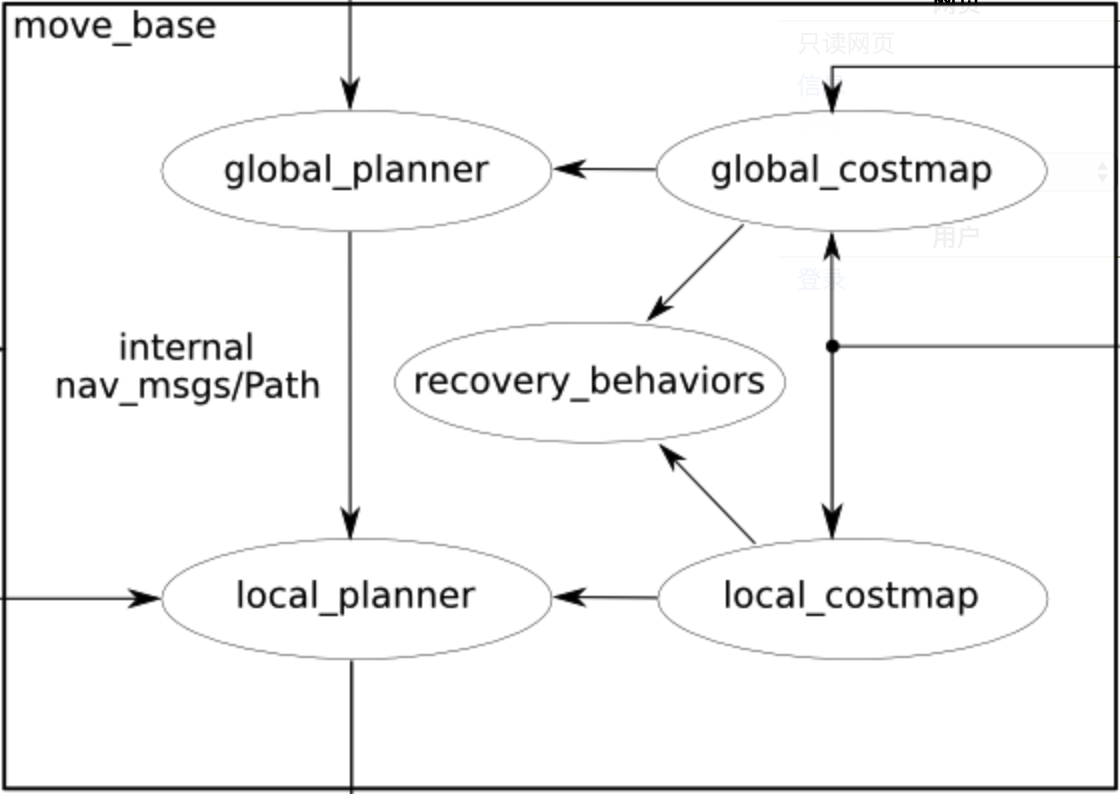
move_base node原理图:
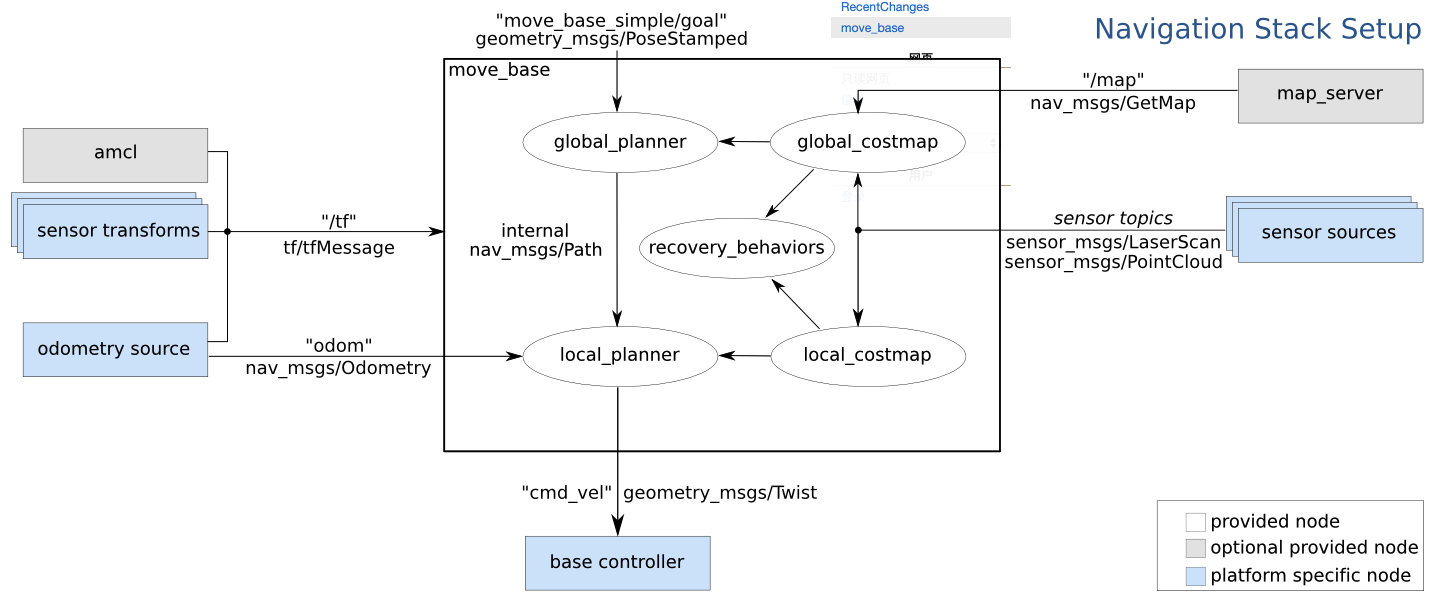
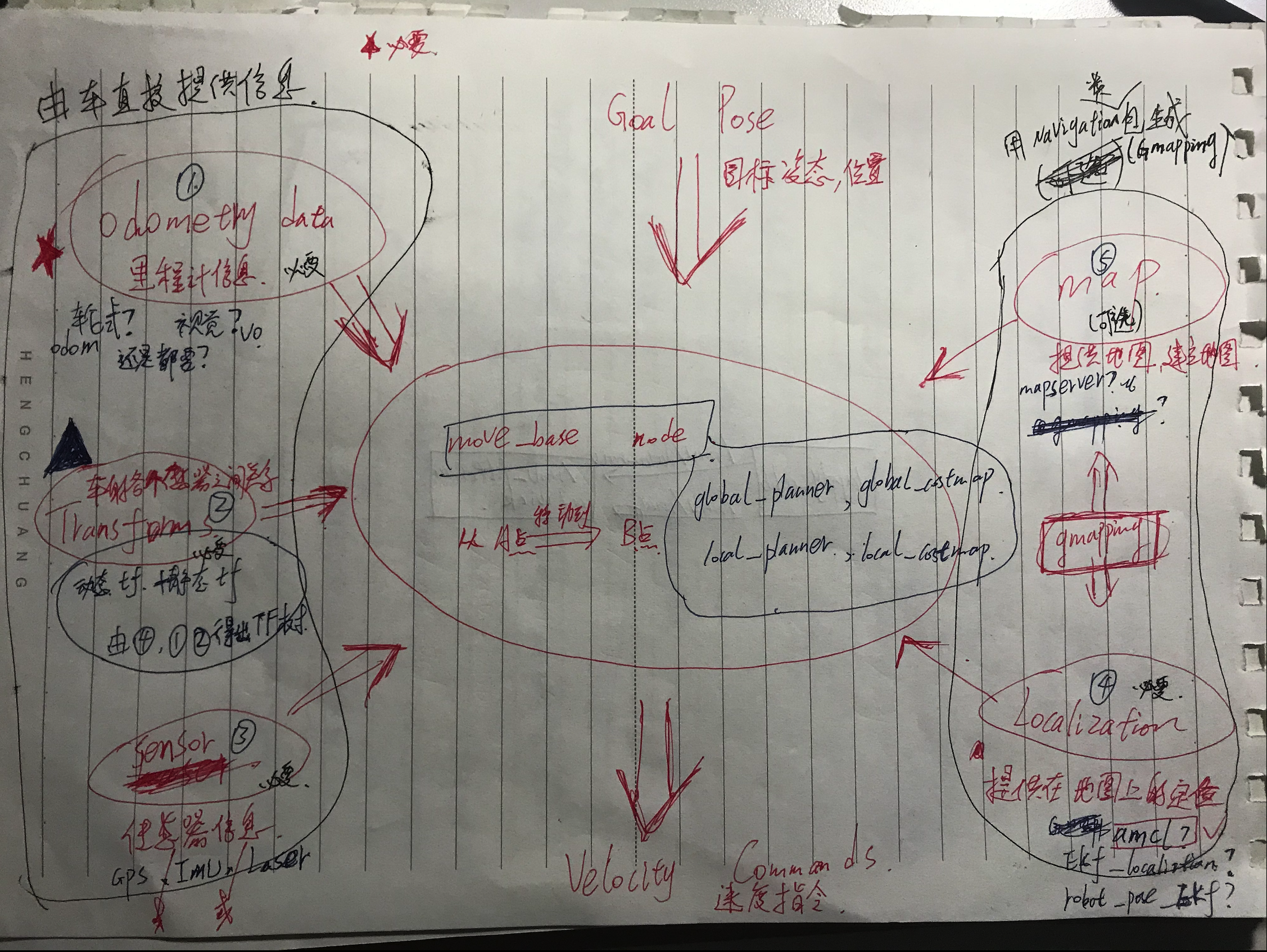
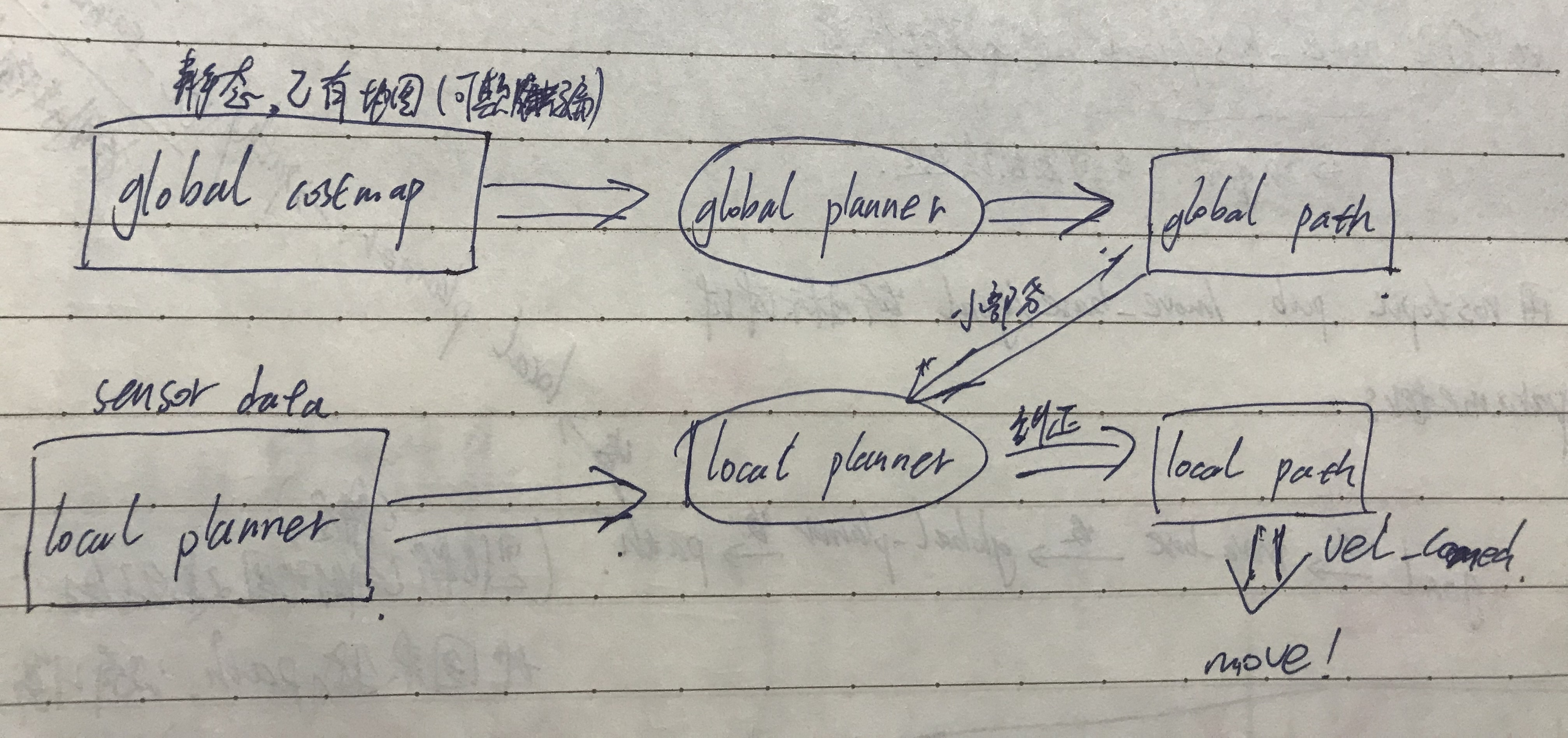
手动整理版:
move_base的搭建是导航的关键,这个框架牵扯到很多的功能包,可以变得非常的复杂。简单来说move_base功能包的作用就是接受一个目标姿态,根据这个姿态给小车点发出速度指令,直到到达目标点。整个导航以及避障的过程都在这个框架中实现。
直接需要提供的信息:
odometry data(里程计信息):
由驱动方法的不同里程计的计算方法也不同,轮、履带、甚至船,都有其不同的计算方法,但是其计算原理都相同,目的是获得小车的里程信息。除了以上机遇电机编码器等里程计计算方法,还有更加复杂更加精确的视觉里程计计算方法,这是计算机视觉通过连续帧的图像信息来得到里程信息的。
TF(坐标变换):
坐标转换关系的建立是分析系统运动学的基础,导航系统的每个传感器以及小车与世界地图左边远点的关系的确定统统可以通过左边转换来实现,因此这是必要的信息,是定位信息以及发送速度指令的基础。这里tf树是由ros操作系统实时维护的,这种tf维护机制是通过广播与监听实现的:两节点发生了位姿关系发生了变化就即时广播出去,ros系统会及时计算并更新所有关联坐标之间的关系,如果要得到某两个坐标之间的位姿信息,就创建监听者实时监听这两个坐标之间的位姿信息。
sensor massege(传感器信息):
在建立地图以及定位的时候,则会依赖传感器的信息,如雷达,imu,gps,camera等。雷达是建立地图必要的传感器信息,也能同时提供定位信息,例如Hector这种算法就只需雷达便可实现SLAM。然而没有里程计的参考,其建图的误差也是非常大的,单靠里程计也不是很理想,所以需要传感器的定位与里程计的定位相配合,减小误差实现更精确的定位与避障,最低的要求也得需要一个雷达。
需要间接提供的信息(功能包提供):
map(地图信息):
这里的地图至世界坐标系和地图信息,世界地图充当基准坐标系的作用,地图信息则用来构建地图,为导航提供定位与障碍以及路径信息。导航时能使用已经建立好的静态地图,也能实时建立地图进行导航。可通过gmapping或map_server实现。
localization(定位信息):
有了地图,小车必须知道自己在什么位置是什么姿态才能进行导航。这里的定位由传感器以及里程计计算得出,主要用的是amcl算法进行定位。可通过gmapping、hector、cartographer等SLAM算法包实现。
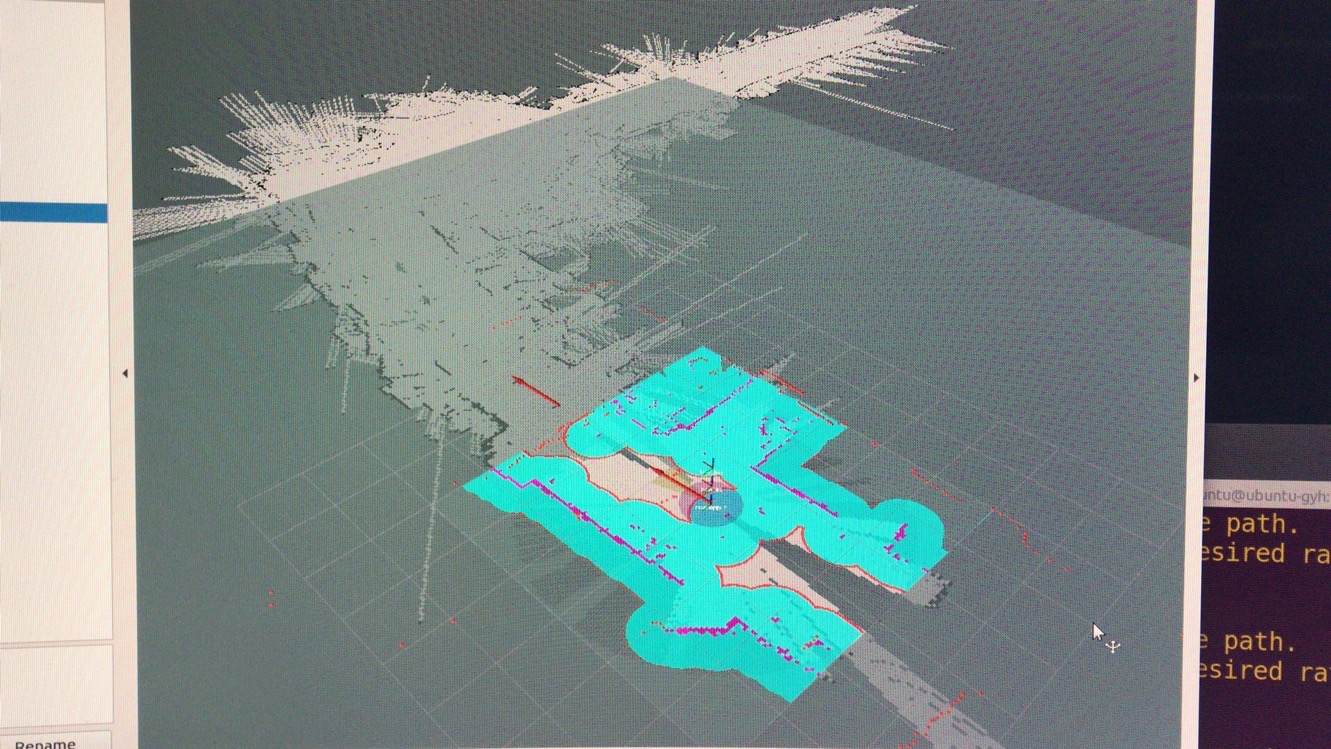
测试方案:tf树以及话题的连接是否合理,rviz里有没有成功发布出相应的全局/局部map以及path主题。
RVIZ:
四、对cost_common_params、global_planner、local_planner、base_local_planner……各项参数的配置,各种配置方案实际对小车的计算效果。
move_base内部结构:
整理版:
前面介绍了要启动move_base所需要的信息与功能包,这里就是具体对move_base功能包里面的参数做配置了。简单来讲在move_base中对目标的导航路线的规划分为了全局规划和局部规划。这两个不同的规划算法相组合,利用所需的信息实现导航和避障的功能。
参照上面的流程图,global_costmap是基于已有的地图(静态地图或者实时地图),由map这个topic得到。然后global planner在此地图信息的基础上计算出小车到目标点的路径,如果是有实时地图的到,那么局部规划器规划出来的路径随着扫描出地图的不断扩大而改变更新。局部地图则不一样,它的地图得使用实时的地图,局部规划器也得参照全局规划器的路径和局部地图进行局部路径的规划,然后下发相应的速度指令,使底盘控制电机运动。对这两个规划器的参数配置则决定了导航效果的好坏。
在move_base节点运行前需要四个配置文件,这些文件定义了一系列相关参数,包括越过障碍物的代价、机器人的半径、路径规划时需要考虑未来多长的路、我们想让机器人以多块的速度移动等等。这四个配置文件分别是:
base_local_planner_params.yaml
costmap_common_params.yaml
global_costmap_params.yaml
local_costmap_params.yaml
base_local_planner_params.yaml:
xxxxxxxxxxcontroller_frequency3.0 # 更新路径规划的频率recovery_behavior_enabledfalse # 复原行为使能clearing_rotation_allowedfalse # 清除旋转允许 TrajectoryPlannerROS# ROS轨迹计划 max_vel_x0.3 # X方向最大速度 min_vel_x0.05 # X方向最小速度 max_vel_y0.0 # 差速轮机器人无Y方向速度,取0 min_vel_y0.0 min_in_place_vel_theta0.5 # 机器人最小原地旋转速度 escape_vel-0.1 # 机器人逃离速度,负值 acc_lim_x2.5 # X方向最大线加速度 acc_lim_y0.0 # 差速轮机器人无Y方向线加速度,取0 acc_lim_theta3.2 # 最大角加速度 holonomic_robotfalse # 全向移动机器人使能 yaw_goal_tolerance0.1 # 至多距离目标方向误差 xy_goal_tolerance0.1 # 至多距离目标位置误差 latch_xy_goal_tolerancefalse # 锁定至多距离目标位置误差 # 全局路径规划和到达目的地之间权重 # 比 gdist_scale 大时,机器人倾向考虑全局路径规划 pdist_scale0.8 # 到达目的地和全局路径规划之间权重 # 比 pdist_scale 大时,机器人倾向考虑到达目的地 gdist_scale0.6 meter_scoringtrue # 以米为单位 occdist_scale0.1 # 避开障碍物的权重 oscillation_reset_dist0.05 #在振荡标志被清零前,机器人必须在出行多远。 publish_cost_grid_pcfalse # 是否使用cost_grid发布 prune_plantrue # 机器人行走1m后,结束动作。 sim_time1.0 # 规划时需要考虑未来多长时间,结合dwa sim_granularity0.025 # 给定轨迹的步长 angular_sim_granularity0.025 # 给定角度轨迹的弧长 vx_samples8 # x方向速度的样本数 vy_samples0 # 差速轮机器人无Y方向速度,取0 vtheta_samples20 # 角速度的样本数,默认为20 dwatrue # 模拟未来轨迹时是否使用动态窗口法
costmap_common_params.yaml:
xxxxxxxxxxobstacle_range2.5 # 障碍物探测距raytrace_range3.0 # 传感器最大探测距离robot_radius0.165 # 机器人半径inflation_radius0.3 # 机器人与障碍物保持的最小距离max_obstacle_height0.6 # 最大障碍物高度min_obstacle_height0.0 # 最小障碍物高度observation_sourcesscan # 观察源,我们这里是激光数据# 观察源的数据类型,发布话题,标记和添加障碍物,scandata_typeLaserScan topic/scan markingtrue clearingtrue
global_costmap_params.yaml:
xxxxxxxxxxglobal_costmapglobal_frame/map # 使用map框架作为global框架robot_base_frame/base_footprint # 机器人最底层框架update_frequency1.0 # 全局地图更新频率,1.0~5.0publish_frequency0 # 发布频率,静态全局地图不需要发布static_maptrue # 是否为静态地图,全局地图一般为静态rolling_windowfalse # 更新全局地图,与上一个参数相反resolution0.01 # 解析度,即地图分辨率transform_tolerance1.0 # tf装换最大延时map_typecostmap # 地图类型
local_costmap_params.yaml:
xxxxxxxxxxlocal_costmapglobal_frame/odom # 使用odom框架作为global框架robot_base_frame/base_footprint # 机器人最底层框架update_frequency3.0 # 局部地图更新频率publish_frequency1.0 # 发布频率,局部地图不要发布static_mapfalse # 是否为静态地图,局部地图一般为动态rolling_windowtrue # 更新局部地图,与上一个参数相反width6.0 # 更新的局部地图的X维长度height6.0 # 更新的局部地图的Y维长度resolution0.01 # 解析度,即地图分辨率transform_tolerance1.0 # tf装换最大延时map_typecostmap # 地图类型
落实配置:
base_local_planner_params.yaml:
xxxxxxxxxxcontroller_frequency3.0recovery_behavior_enabledfalseclearing_rotation_allowedfalseTrajectoryPlannerROS max_vel_x0.3 min_vel_x0.05 max_vel_y0.0 # zero for a differential drive robot min_vel_y0.0 min_in_place_vel_theta0.5 escape_vel-0.1 acc_lim_x2.5 acc_lim_y0.0 # zero for a differential drive robot acc_lim_theta3.2 holonomic_robotfalse yaw_goal_tolerance0.1 # about 6 degrees xy_goal_tolerance0.1 # 10 cm latch_xy_goal_tolerancefalse pdist_scale0.9 gdist_scale0.6 meter_scoringtrue heading_lookahead0.325 heading_scoringfalse heading_scoring_timestep0.8 occdist_scale0.1 oscillation_reset_dist0.05 publish_cost_grid_pcfalse prune_plantrue sim_time1.0 sim_granularity0.025 angular_sim_granularity0.025 vx_samples8 vy_samples0 # zero for a differential drive robot vtheta_samples20 dwatrue simple_attractorfalse
costmap_common_params.yaml:
xxxxxxxxxxobstacle_range2.5raytrace_range3.0robot_radius0.1inflation_radius0.1footprint-0.50 -0.60 -0.50 0.60 0.50 0.60 0.50 -0.60track_unknown_spacetruemax_obstacle_height0.6min_obstacle_height0.0transform_tolerance5.00 #original:0.13observation_sourcesscanmap_typecostmapscansensor_framebase_laser data_typeLaserScan topic/scan markingtrue clearingtrue
global_costmap_params.yaml:
xxxxxxxxxxglobal_costmap global_framemap robot_base_framebase_footprint update_frequency3.0 publish_frequency5.0 static_maptrue rolling_windowfalse resolution0.01 transform_tolerance0.8 map_typecostmap
local_costmap_params.yaml:
xxxxxxxxxxlocal_costmap global_frameodom robot_base_framebase_footprint update_frequency3.0 publish_frequency5.0 static_mapfalse rolling_windowtrue width5.0 height5.0 resolution0.01 transform_tolerance1.0 map_typecostmap cost_scaling_factor5 inflation_radius0.2
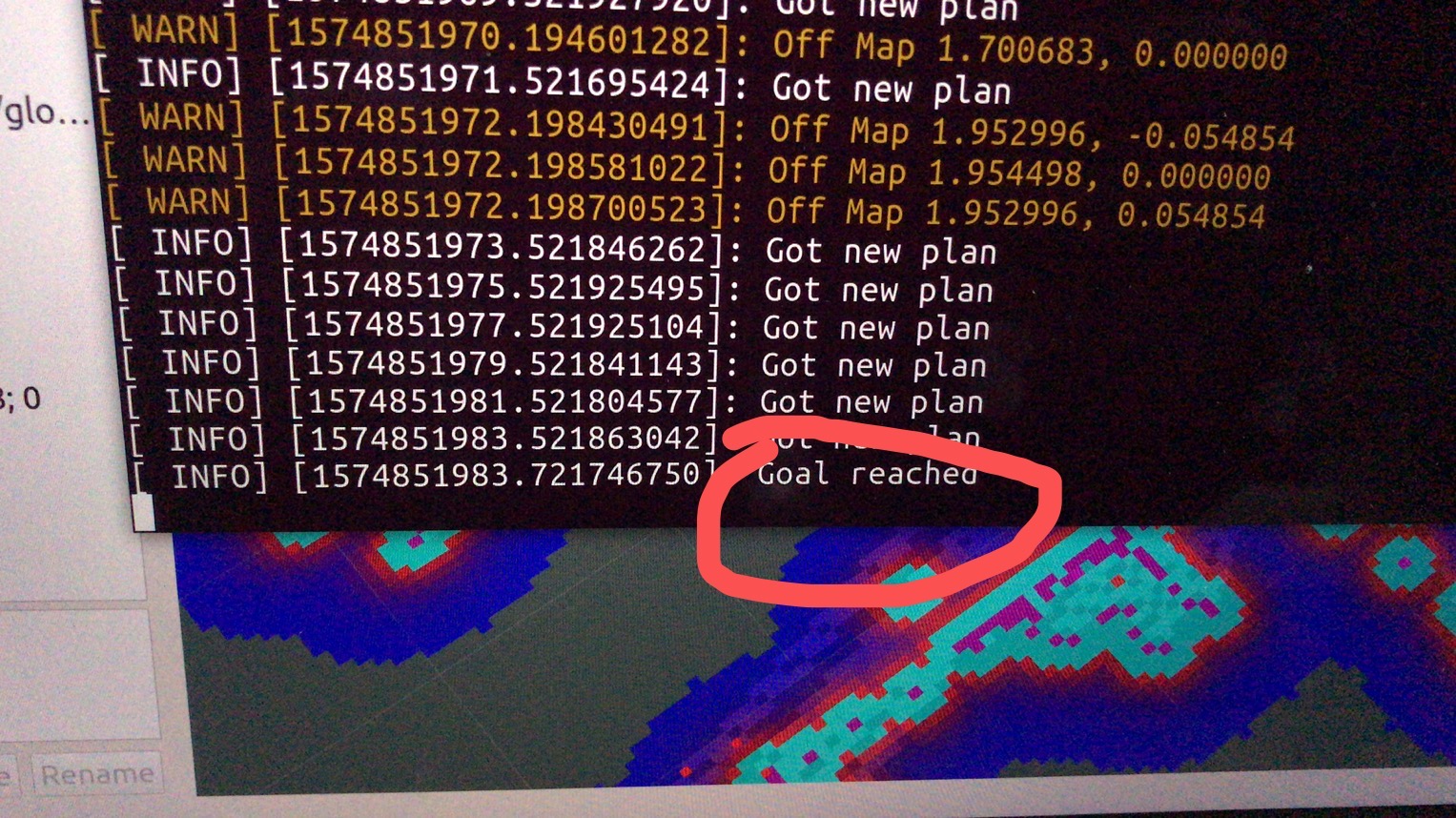
测试方案:move_base没有发出实时变化的速度指令(/cmd_vel),全局/局部规划的膨胀地图以及相应的路径线条是否能够显示,小车坐标在规划处路径之后能够正常移动,同时局部规划路径出现。发送简单的直线目标点能够到达,move_base节点显示goal reached!,简单避障效果的测试。
路径规划:
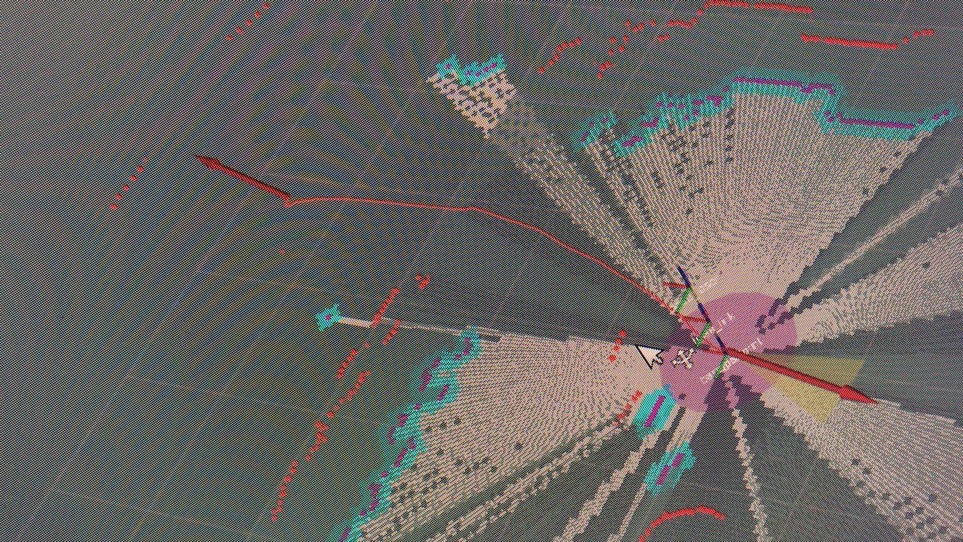
goal reached: